Hard Disk Drive Basic Knowledges
What is A Hard Disk Drive?
Hard Disk or sometimes called a Hard Drive(HDD, hard drive, hard disk, fixed drive, fixed disk, fixed disk drive) is the main storage space inside your PC.
An HDD consists of one or more rigid ("hard") rapidly rotating discs (platters) with magnetic heads arranged on a moving actuator arm to read and write data to the surfaces. These platters are locked away inside a steel casing as unclean air can easily ruin a hard disk.
HDD Connection Types
There are currently 3 connections for a hard disk. IDE (or ATA) SCSI and Serial ATA.. The most common is the IDE interface. This provides an 80 pin connection to most standard motherboards and you can't normally go wrong buying an IDE drive for your machine. SCSI connections often require extra hardware unless its built into your motherboard. SCSI hard disks are often faster but more expensive than there IDE counterparts. The final type is the newest type. Serial ATA does away with parallel data transfer which has its problem of large wires and electrical interference. The Serial ATA standard is more reliable and uses smaller un-obtrusive wires. Smaller wires also means better air flow for your case.
1. Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment (PATA)
These types of drives are also known as Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) and Enhanced Integrated Drive Electronics (EIDE) drives. These drives utilize either a 40 or a 80 wire cable with a broad 40-pin connector. 40 wire cables are utilized in older and slower hard disks, whereas 80 wire cables are used in faster ones. Nowadays, these types of hard disks are being substituted by SATA hard disks.
2. Serial ATA (SATA)
These hard disks use a totally different connector than their PATA counterparts. Moreover, they also employ a different power adapter than IDE ones, though adapters are easily attainable. The main difference between a SATA and a PATA hard disk is that the former is thinner and purportedly have a faster data interface than the latter. Nevertheless, this speed dissimilarity is not distinguishable in PATA and SATA drives which have the same rpm rating. SATA drives are more efficient, and use less power than PATA ones.
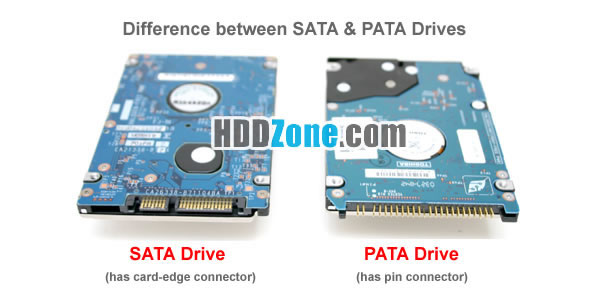
SATA Vs PATA Hard Drives
These hard disks are similar to IDE hard drives. They also spin at a higher rate in comparison to IDE and SATA ones. IDE and SATA drives generally spin at 7,200 rpm, whereas SCSI ones spin at 10,000 to 15,000 rpm. Today, SATA drives featuring a speed of 10,000 rpm are also manufactured. The higher the rpm, faster is the data access, but it may also lead to a faster breakdown.
4. Solid State Drives (SSD)
The newest technology in Hard drives is the SSD or Solid State Drive. Unlike the electromechanical types of hard drives, the SSD drive has no moving parts. No moving parts means that they are silent. SSD drives can be found with either the IDE type connector or the SATA type connector which are more expensive.

HDDs Vs SSDs
HDD Form factors
The 2.5 and 3.5 are inches and they usually designate the diameter of the disk itself and not the housing. The enclosure will (of course) always be larger than that.
1.8 inch: Outer measure 2.12 in x 0.314 in x 2.795 in (54 mm x 8 mm x 71 mm). These can be used for Solid State Drives but the disk itself also in iPods, etc.
2.5 inch: Outer measure 2.75 in x 0.275 - 0.59 in x 3.945 in (69.85 mm x 7 - 15 mm x 100 mm). These are used in notebooks and also can be used for Solid State Drives.
3.5 inch: Outer measure 4 in x 1 in x 5.75 in (101.6 mm x 25.4 mm x 146 mm). Those are mostly used in desktop PCs.
Six HDDs with 8", 5.25", 3.5", 2.5", 1.8", and 1" hard disks with a ruler to show the length of platters and read-write heads
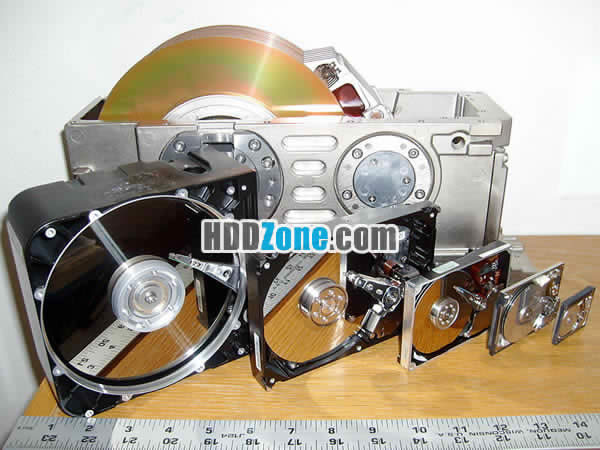

Hard Drive Form Factors
Popular Hard Disk Drive Manufacturers:
Seagate, Western Digital, Toshiba...
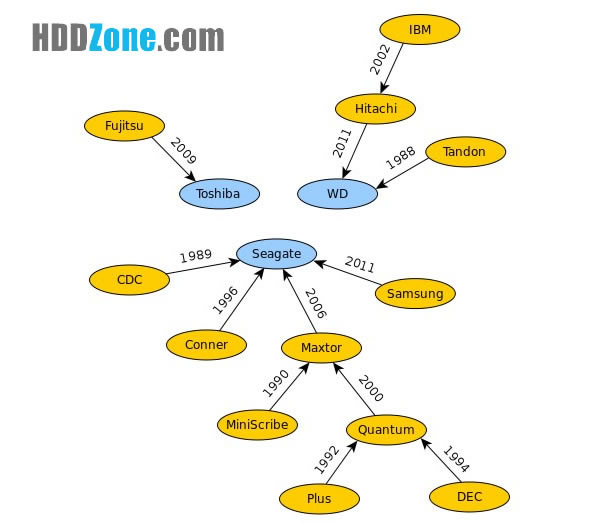
Hard Drive Manufacturers
Basic Hard Disk Drive Components
Many types of hard disks are on the market, but nearly all drives share the same basic physical components. Some differences may exist in the implementation of these components (and in the quality of materials used to make them), but the operational characteristics of most drives are similar. Following are the components of a typical hard disk drive:
- Disk platters
- Logic board
- Read/write heads
- Cables and connectors
- Head actuator mechanism
- Configuration items (such as jumpers or switches)
- Spindle motor
- Bezel (optional)
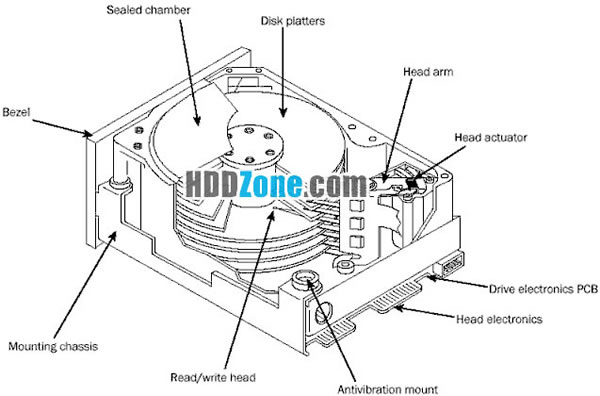
Hard Drive Components
The platters, spindle motor, heads, and head actuator mechanisms usually are contained in a sealed chamber called the Head Disk Assembly (HDA). The HDA usually is treated as a single component; it rarely is opened. Other parts external to the drive's HDA -- such as the logic boards, bezel, and other configuration or mounting hardware -- can be disassembled from the drive.
Measuring the Speed of a Hard Disk
There are various ways of measuring the speed of the hard disk. The main ones are the maximum data transfer rate, the spindle rotation speed and the seek time.
1. Maximum Transfer Rate - This is the highest amount of data that can be transferred per second. Common forms of hard disks come with an ATA format. the speed rating of an ATA100 disk would be 100Mb/s. Likewise a ATA66 disk would be able to transfer a maximum of 66Mb/s.
2. Spindle Rotation Speed - The rotation speed of the disk really is the basis of the other two factors of hard disk speed. The faster the rotation speed, the more data can be written per second and the quicker it is to find the correct data on the platter.
3. Seek Time - The seek time of a hard disk is the average time it takes for the disk to find the data you need on the platters. A fast spinning, highly accurate and responsive disk will have a shorter seek time and will perform much better, especially when the data is scattered around the disk.
Back to Home: HDD PCB Rescources




